Specific Heat Capacity
Specific Heat Capacity: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Heat Capacity of Solids,Definition of a Calorie,Specific Heat Capacity of Water, etc.
Important Questions on Specific Heat Capacity
A heater melts ice in a bucket completely into water in minutes and then evaporates all that water into steam in minutes sec. If latent heat of fusion of ice is , latent heat of steam will be (specific heat of water is )?
A metal cube absorbs of heat when its temperature is raised by . If the specific heat of the metal is , then the mass of the cube is
An immersion heater is rated . It should heat litre of water from to in about. (Specific heat of water is , density of water is )
The volume of moles of an ideal gas with degree of freedom is varied according to the law where is a constant. The molar specific heat of the gas at constant pressure is
A diatomic gas expands from to as shown in the P-V graph. For this process choose the correct statement
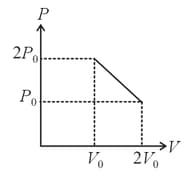
The piston is massless and the spring is ideal and initially streched the piston cylinder arrangement encloses an ideal gas. If the gas is heated quasistatically the graph.
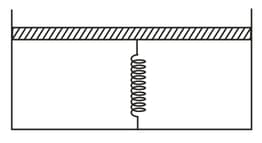
A -tube, made of heat- insulating material, is shown in figure. One limb is closed by a non- conducting cork, the temperature is . How much heat (in multiples of Joule) is required to be given by the coil so that the air rises to a temperature ? The thermal expansion of mercury is negligible. (Take:
Area of the tube as of SI units). Neglect the heat flow through the mercury.
An ideal gas which undergoes through a process starting at and ends at . is a constant. The molar heat capacity of the gas if it is monoatomic is ; What is ?
Define one calorie. How it is related to joule?
An ideal diatomic gas of moles and with initial pressure and volume undergoes a thermodynamic process. In this process the pressure is directly proportional to volume and the rms speed of the molecules is doubled. Then, the amount of heat required in this process is
Define of heat. What is the relation between Joule and calorie?
At a given temperature, the specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is always greater than its specific heat at constant volume.
Molar specific heat at constant pressure is related to internal energy and absolute temperature as ________
and are specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume respectively. It is observed that, for hydrogen gas and for nitrogen gas. The correct relation between and is:
Assertion: The specific heat at constant pressure is greater than the specific heat at constant volume i.e., .
Reason: In case of specific heat at constant volume, the whole of heat supplied is used to raise the temperature of one mole of the gas through while in case of specific of heat at constant pressure, heat is to be supplied not only for heating 1 mole of gas through but also for doing work during expansion of the gas.
An insulated box containing a diatomic gas of molar mass is moving with velocity . The box is suddenly stopped. The resulting change in temperature is . What will be the value of ?
If and denote the specific heats of nitrogen gas per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively, then
Define molar specific heat capacity at constant volume and pressure.
